Parking Garages
Continuous monitoring of carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide from vehicle exhaust in enclosed parking facilities ensures breathable air quality and enables VFD demand-controlled ventilation to reduce energy costs.
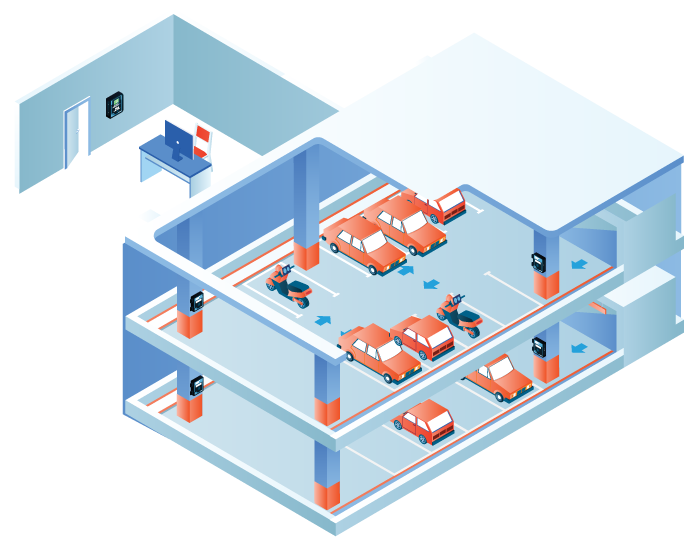
Typical Parking Garages System
Target Gases
Gases monitored in this application
Why Gas Detection is Required
Parking garages that are enclosed or underground require dedicated gas detection systems to protect occupants from vehicle exhaust and to comply with mechanical and building codes. Because vehicles are continuously entering, exiting, idling, and circulating, exhaust gases can accumulate rapidly without effective monitoring and ventilation. Modern underground parking gas detection systems combine continuous sensing with automated ventilation control to maintain safe air quality while minimizing unnecessary energy use. The primary gases of concern in parking garages are carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), which are produced by gasoline and diesel vehicles. CO is colorless and odorless and can cause serious health effects at relatively low concentrations, while NO₂ is a respiratory irritant commonly associated with diesel exhaust. Emission levels vary throughout the day based on traffic volume, vehicle type, and idling duration, making continuous monitoring with parking garage CO detectors and NO₂ sensors essential. Sensors are typically distributed throughout the garage, including ramps, entrances, exits, and high traffic areas, to ensure localized detection and response. In certain circumstances, combustible gas monitoring may also be required in parking garages. This applies to facilities that accommodate natural gas or propane powered vehicles, fleet vehicles with onboard fuel systems, or garages that include vehicle service, maintenance, or fueling functions. In these cases, methane or propane detectors provide early warning of fuel leaks that could create fire or explosion hazards. Combustible gas detection is generally supplemental and applied only where specific fuel related risks exist, rather than as a standard requirement across all parking garages. Ventilation control is a critical part of parking garage gas detection strategy. Traditional systems often rely on continuously running exhaust fans or fixed schedules, which results in significant energy waste. Demand controlled ventilation (DCV) uses real time gas concentration data from CO and NO₂ sensors to automatically adjust ventilation based on actual conditions. When gas levels rise, exhaust fans activate in the affected zones, and when levels return to safe limits, fan operation is reduced or shut off. This approach ensures safe air quality while avoiding unnecessary ventilation during low traffic periods. The energy impact of DCV is substantial. Ventilation is typically the largest energy load in enclosed parking garages and switching from continuous operation to sensor based control can reduce ventilation energy costs by 70–90 percent. Additional benefits include reduced fan wear, lower maintenance requirements, and decreased heating and cooling losses caused by excessive exhaust. These savings make parking garage gas detection with DCV one of the most cost effective upgrades for parking facilities. Parking garage gas detection and ventilation requirements are supported by established codes and standards. The International Mechanical Code (IMC) Chapter 404 allows reduced ventilation rates when CO and NO₂ monitoring with automatic fan control is provided, and ASHRAE Standard 62.1 recognizes contaminant based ventilation strategies for enclosed parking garages. Compliance with these standards is typically achieved by integrating gas sensors directly with the ventilation system rather than relying on constant full capacity airflow. Modern parking garage gas detection systems are commonly integrated with building automation systems using BACnet or similar protocols. This integration enables centralized monitoring, alarm reporting, trend logging, and coordinated fan control across multiple garage levels or zones. It also simplifies commissioning, inspection, and ongoing compliance documentation.
ParkSense™
Code-Compliant Parking Garage Monitoring
Navigate complex regional codes with our pre-engineered detection systems designed for your jurisdiction. ParkSense solutions simplify compliance with IMC, CMC, and local regulations.
Download ParkSense Solution Guide
Request a Quote
System Architecture
A complete underground parking garage gas detection system typically consists of distributed CO and NO2 gas detectors connected to a central controller. The controller monitors gas levels across all zones and manages VFD ventilation fan operation—running fans only when gas levels require it instead of continuously, reducing ventilation costs up to 70-90%. For smaller facilities, self-contained units combine detection and control in a single device. Larger installations benefit from networked architectures with digital communication between detectors and controllers, enabling advanced diagnostics and integration with building management systems.
Key Considerations
Important factors for planning your system
Gas detection system operates ventilation systems on-demand for energy efficiency
One gas detector provides coverage of up to 5,000 ft² / 50 m radius with 360-degree coverage
Alternate fuel vehicles that use natural gas, methanol, ethanol, etc. also produce carbon monoxide exhaust, however combustible gas detection is recommended
System can integrate with building automation systems for comprehensive facility management
Detectors should be mounted in the breathing zone (4-6 ft from floor)
Additional Information
Where to Mount CO and NO₂ Gas Detectors for Diesel Exhaust Applications For vehicle exhaust applications that include diesel exhaust, Carbon Monoxide and Nitrogen dioxide sensor combination gas detectors should be used to monitor the hazardous gas levels in the enclosed space. Carbon monoxide is about the same density as air and will readily disperse throughout an area where there may be some air movement and activity persisting in the breathing zone (4–6 ft from the floor). Nitrogen dioxide gas is heavier than air, but often hot, as in exhaust fumes, it will rise. As the exhaust cools, the gas will dissipate and fall downwards, settling throughout the breathing zone. In enclosed spaces that have diesel vehicles with bumper height exhaust, the hot exhaust will not reach the ceiling before cooling and settling in the breathing zone. As a result, the Carbon monoxide and Nitrogen dioxide will be present quite quickly in the breathing zone. Environments that have vehicle repair pits should have a Nitrogen dioxide gas detector mounted in the pit: the gas may pool into the area. Carbon monoxide and Nitrogen dioxide sensors should always be mounted in the breathing zone. People occupy the breathing zone; therefore, this is the area that needs to be monitored for health and safety reasons.
Related Products

LPT Low Power Transmitter

cGas Detector Analog Transmitter

ESH-A Remote Sensor

cGas Detector Digital Transmitter
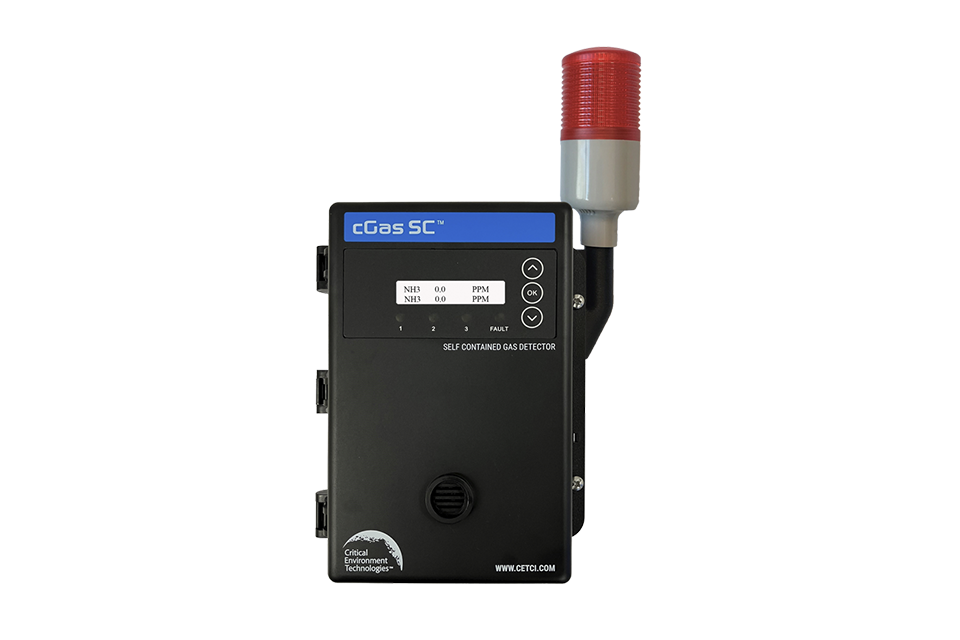

cGas-SC Self-Contained Controller
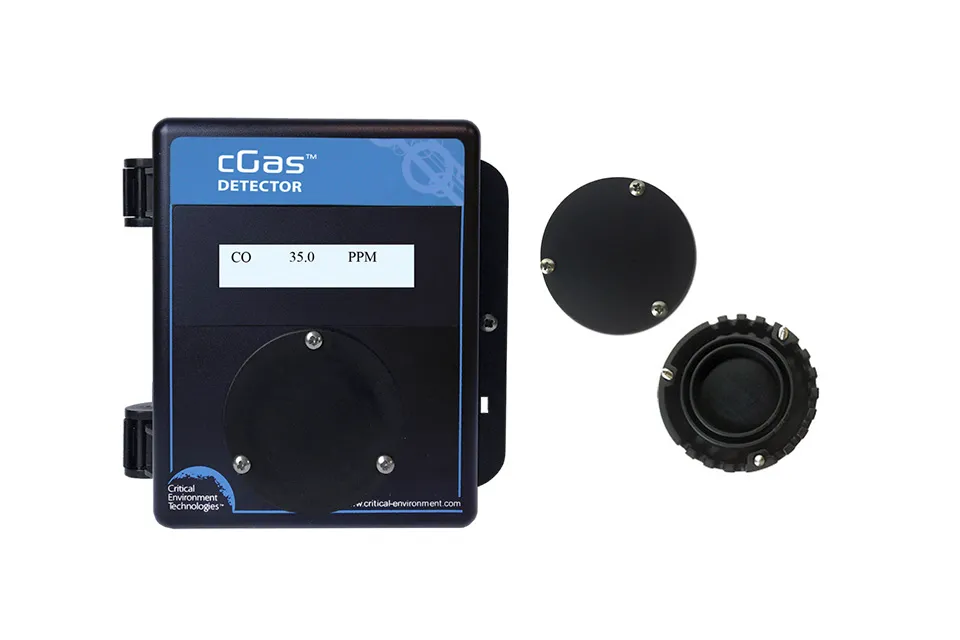

Splash Guard (Option -S)
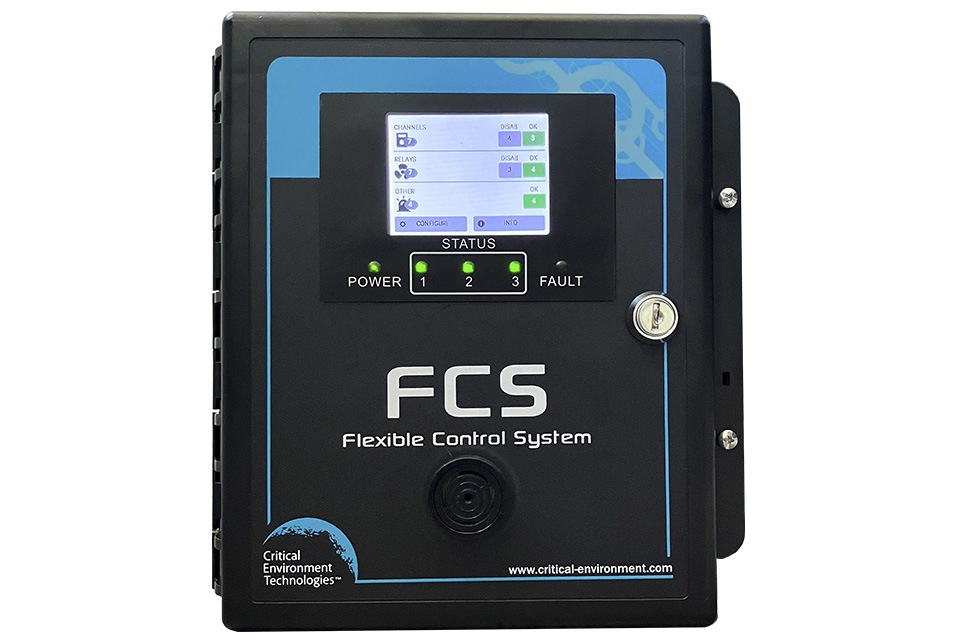

FCS Multi Channel System Controllers
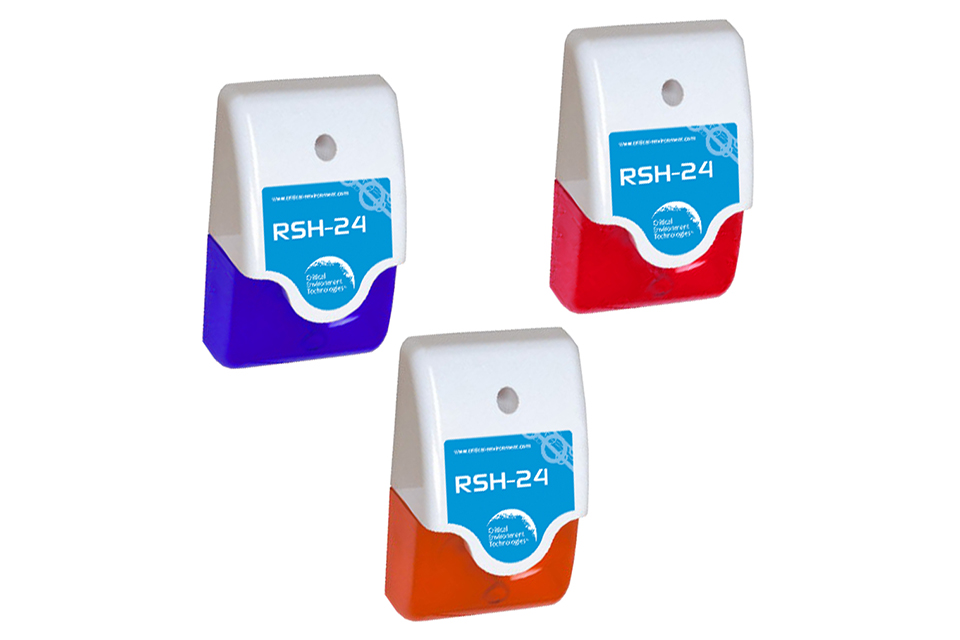

RSH-24V Remote Strobe & Horn